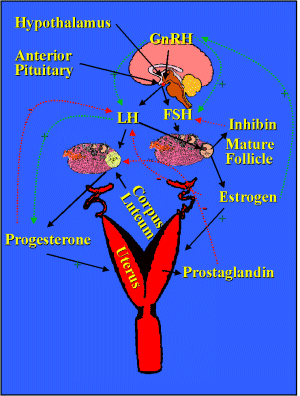
Gonadotropin
Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
- Decapeptide.
- Released from the hypothalamus.
- Estrogen surge causes its release.
- Currently thought to cause the release of the
both gonadotropins, Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle
Stimulating Hormone (FSH), but there may actually be an LH
releasing hormone (LHRH) and an FSH releasing hormone FSHRH.
LH
and FSH
- Gonadotropins (they affect the gonads - 'trope
the gonads').
- Released from same cells in anterior
pituitary (may even be in the same
granules within the cell).
- Glycoprotein structure (carbohydrate and protein). This
means they are antigenic and will degrade.
- Structure: 2 subunits
- Alpha - same within
species i.e. LH, FSH, TSH have same alpha unit within a species.
- Beta - same between species i.e. LH in all species have same beta
unit.
- Mechanism of action:
- Bind cell membrane and
cause cAMP production
- Causes phosphorylation in cell.
- Fast
action results.
FSH
- Causes growth of follicles past antral stage.
- Causes stimulation of granulosa cells in the
ovary.
- Stimulates establishment of LH receptors on
granulosa cells.
- Suppressed by inhibin which is produced by the
large follicles.
- The pulse frequency probably initiates subsequent
events in the cycle.
- Half life of 60 minutes
- Secreted at same time as LH, but other peaks
during cycle may choose follicle for next cycle in polyestrous
species.
LH
- Binds to receptor on follicles and corpus luteum.
- Causes ovulation and luteinization of follicle
about 24-48 hrs after release. (May cause ovulation by causing
collagenase release that breaks down the follicle and then stimulates
progesterone release to actually cause ovulation.)
- Stimulates progesterone production by corpus
luteum.
- Half life 22 minutes.
- Involved in puberty and seasonal cyclicity.
- Anestrus - hi freq., low amp.
- Cycling - hi amp., lo freq.
- Inhibited by low concentrations of estrogens and
progesterone during diestrus.
- hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) has similar
action and is used clinically to induce ovulation in mares.
Steroid hormones
- Mechanism of action:
- Bind cytosol receptor.
- Transferred to nucleus.
- mRNA produced .
- Changes cellular
machinery.
- A slower process than gonadotropins.
Follicle
on ovary
- Oocyte is arrested at the end of prophase in meiosis.
- LH is needed to restart oocyte development.
- FSH starts follicular growth past antral stage.
Estrogen
(estradiol 17 beta).
- From granulosa cells in follicles.
- Causes LH and FSH surges via GnRH release.
- 'Primes' uterus.
- Causes estrous behavior.
Corpus luteum
(yellow body) on ovary.
Progesterone
- Steroid.
- Two compartment theory of production.
- Stimulate uterine secretions.
- Stimulates estrogen receptors
- Inhibit uterine motility
- Decrease uterine immunity
- Inhibit LH and FSH
- Needed to maintain pregnancy
Inhibin
- Peptide produced by granulosa cells in growing
follicle.
- Inhibits FSH release and possibly FSH binding to
granulosa cells.
- Alpha-1 + beta-A or beta - B - inhibits FSH.
- Beta -A + beta-B cause FSH stimulation.
Oxytocin
- Mostly released from posterior pituitary.
- Causes uterine contractions.
- Released from bovine corpus luteum.
- Causes prostaglandin release and luteolysis.
Prostaglandin
(PGF2alpha)
- 20 carbon acid.
- Secreted by uterus in some animals to cause
luteolysis.
|
Click on the picture to get an
enlarged view of the picture.





|
|